

Under the proposed addendum, an alternative set of efficiency levels, Path B, is established for water-cooled chillers intended for applications where significant time is expected at part load. The use of VSDs has led to off-design and part-load improvement of the chiller’s performance with efficiencies of up to 30% in integrated part-load value (IPLV). Variable speed drives (VSD) technology has advanced and is finding widespread application in water-cooled chillers. Product development for water-cooled chillers in recent years has focused on improving off-design and part-load performance where most of the operating hours occur, said Drake Erbe, chair of the standard’s mechanical subcommittee. The proposed addendum was developed by a team of Standard 90.1 members, industry manufacturers and energy advocacy groups, including the American Council for an Energy Efficiency Economy, Washington, D.C., and the Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration Institute (ARI), Arlington, Va., and was supported by ARI chiller manufacturers. 1, 2010, an additional path of compliance for water-cooled chillers as well as consolidation and new requirements for some of the existing categories. Fourteen proposed addenda to the 2007 standard, due out for publication later this year, currently are open for public comment.Īmong the addenda is proposed addendum m, which establishes effective Jan.
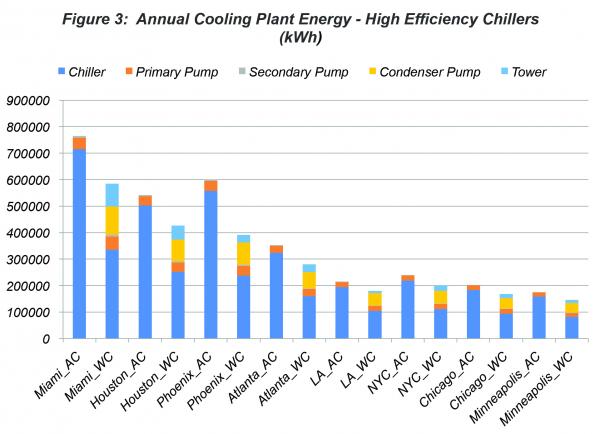
An estimated annual energy savings of 13% relative to ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-2004 should result from a proposed addendum regarding air- and water-cooled chillers.ĪNSI/ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1, Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings, provides minimum requirements for the energy-efficient design of buildings except low-rise residential buildings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
